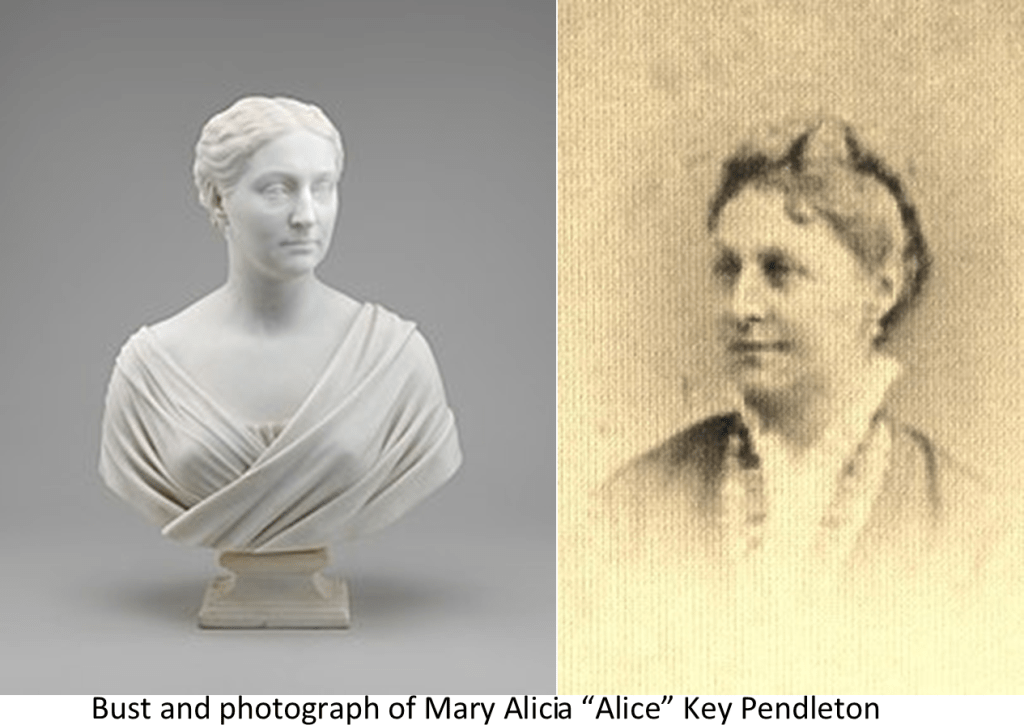
A person, whom I’ve never met and whose name I’m not divulging for fear of reprisal to him, wrote to me about my being banned from Facebook for Wrong Think.
Hi Tom, sorry to hear about being banned from Facebook, for no reason at all, and not being able to dispute it. I will back you up by saying that of the thousands of student files I’ve read, I’d say that well over 90% of the students were appreciative of their time at “Dear Old Carlisle”, and you would be hard pressed to find negative comments in those same records. That being said, there were “runners” for sure, which I understand, Carlisle wasn’t for everyone. These ignorant, on the subject of the Carlisle Indian School, virtue signalers, who just parrot the same old “all Indian schools were evil” narrative, don’t have a clue, and do the Carlisle students a serious misjustice by not learning the good it did. People need to realize that a census done in the late 1890’s, early 1900’s accounted for maybe 225,000 Indigenous folks left, Capt. Pratt was on a mission, not to let their extinction happen.
I haven’t read thousands of student files because my interest lies primarily with the football team. However, I have read hundreds of files of players and their relatives. Families often sent several or all of their children to Carlisle and information on the players’ family histories, particularly with regard the health and deaths, could be found in siblings’ files. I will concede that former students who had unhappy experiences at Carlisle would have been unlikely to respond to requests from the administration about their lives after Carlisle. Also, administrators may have purged negative responses from the files. In spite of that, a huge number of positive responses can still be found in the archives over 100 years after the school closed.